# Set up your query
After you've set up your data source, continue with SQL Transformations by setting up your query.
# Prerequisites
# Set up your query
After specifying a data source, you can define the query that acts on the data. Query inputs in SQL Transformations support all standard operations offered by a standard SQL query engine.
# Example query setup
The following query merges the employee and zipcode tables together based on the zipcode column in both the tables.
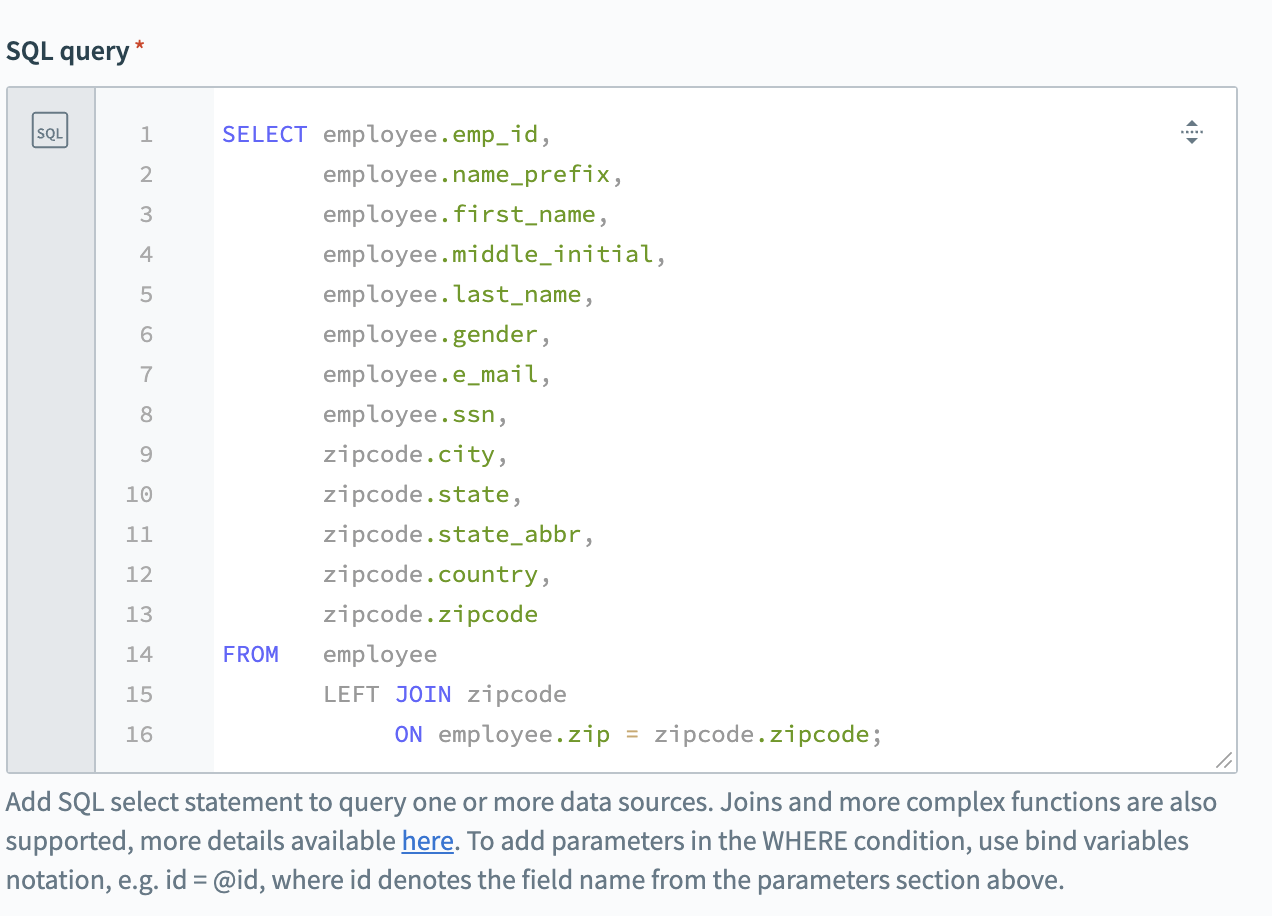 Example query setup
Example query setup
CAPITALIZATION
In the preceding example, all of the CSV headers are lowercase. If your query contains capitalized CSV headers, you must enclose the capitalized headers in quotation marks ("").
For example:
SELECT distinct test."PropertyId", test."Tract_Business" FROM test ORDER by test."PropertyId" LIMIT 1 OFFSET 2
# Supported operations
The following section contains lists of supported and unsupported data types, syntax clauses, subqueries, and functions in SQL Transformations.
# Data types
Character types
- CHAR
- VARCHAR
- TEXT
Numeric types
- TINYINT
- SMALLINT
- INT or INTEGER
- BIGINT
- TINYINT
- UNSIGNED
- SMALLINT UNSIGNED
- INT UNSIGNED or INTEGER
- UNSIGNED
- BIGINT UNSIGNED
- FLOAT
- REAL
- DOUBLE
- DECIMAL (precision, scale)
Date/Time types
- DATE
- TIME
- TIMESTAMP
Boolean types
- BOOLEAN
Binary types
- BYTEA
# Unsupported data types
Unsupported types
- UUID
- BLOB
- CLOB
- BINARY
- VARBINARY
- REGCLASS
- NVARCHAR
- STRING
- CUSTOM
- ARRAY
- ENUM
- SET
- INTERVAL
- DATETIME
# Syntax clauses
Select syntax clauses supported
- WITH
- SELECT
- FROM
- WHERE
- JOIN
- GROUP BY
- HAVING
- UNION
- ORDER BY
- LIMIT
# Subqueries
Select subqueries supported
- EXISTS
- NOT EXISTS
- IN
- NOT IN
# Aggregate functions
General
- min
- max
- count
- avg
- sum
- array_agg
Statistical
- var / var_samp / var_pop
- stddev / stddev_samp / stddev_pop
- covar / covar_samp / covar_pop
- corr
Approximate
- approx_distinct
- approx_median
- approx_percentile_cont
- approx_percentile_cont_with_weight
# Scalar functions
Math functions
- abs(x)
- acos(x)
- asin(x)
- atan(x)
- atan2(y, x)
- ceil(x)
- cos(x)
- exp(x)
- floor(x)
- ln(x)
- log10(x)
- log2(x)
- power(base, exponent)
- round(x)
- signum(x)
- sin(x)
- sqrt(x)
- tan(x)
- trunc(x)
Conditional functions
- coalesce
- nullif
String functions
- ascii
- bit_length
- btrim
- char_length
- character_length
- concat
- concat_ws
- chr
- initcap
- left
- length
- lower
- lpad
- ltrim
- md5
- octet_length
- repeat
- replace
- reverse
- right
- rpad
- rtrim
- digest,
- split_part
- starts_with
- strpos
- substr
- translate
- trim
- upper
Regular expression functions
- regexp_match
- regexp_replace
Temporal functions
- to_timestamp
- to_timestamp_millis
- to_timestamp_micros
- to_timestamp_seconds
- extract
- date_part
- date_trunc
- date_bin
- from_unixtime
- now
Other functions
- array
- in_list
- random
- sha224
- sha256
- sha384
- sha512
- struct
- to_hex
# Read next
SAMPLE USE CASES
See our guides for step-by-step instructions on how to leverage SQL Transformations for the following use cases:
Last updated: 10/27/2023, 1:52:49 AM