# JSON Web Token
You can use JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for additional security. This is a standard RFC 7159 (opens new window) for web authentication. JWT are signed using a secret or key selected by the manager of the access profile.
JWT are used by identity providers (IdP), such as Okta, OneLogin, and Auth0, to authenticate users and provide verified access to business applications. Also known as Single-Sign On, identity providers streamline access to applications through a central authentication mechanism.
You can sign your JWT to verify that the key is legitimate. This allows the recipient to validate that the contents are unmodified, adding another layer of security.
# Supported signing methods
Workato supports two signing methods:
| Signing method | Description |
|---|---|
| HMAC | HMAC uses a symmetric shared secret (client and server have the same secret). This uses a 256-bit secret value. |
| RSA | RSA uses an asymmetric key pair (client has a private key and shares the public key with the server). |
# HMAC signing method
If you select HMAC, you will see the following fields in the Access Profile screen:
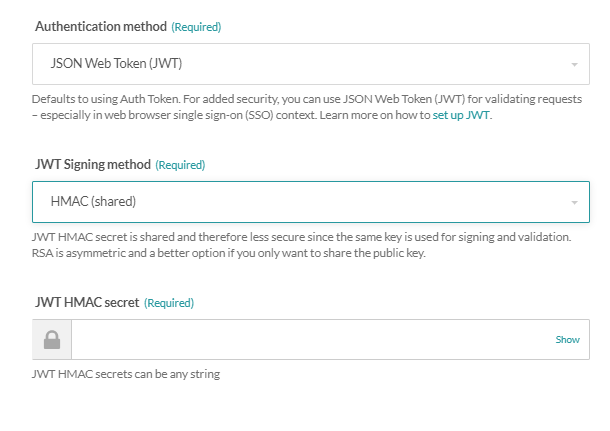 JWT Configuration HMAC authentication
JWT Configuration HMAC authentication
# Generate an HMAC secret
The shared secret can be any value that you select, but for best security, it should be a long value generated by a secure random number generator.
Use OpenSSL to generate a secret:
openssl rand -base64 32
Paste the secret value into the JWT HMAC secret field.
# RSA signing method
If you select RSA, you will see the following fields in the Access Profile screen:
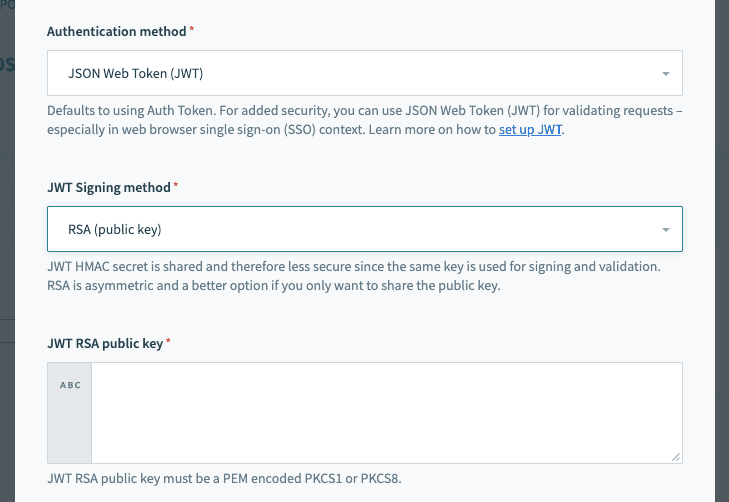 JWT Configuration RSA authentication
JWT Configuration RSA authentication
# Generate an RSA public/private key pair
To configure RSA authentication, you must have an RSA public key/certificate and a corresponding RSA private key.
Use ssh-keygen to generate a key pair.
When prompted for a passphrase, leave it empty:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -m PEM -f jwtRS256.key
This will generate two files, one for the private key and one for the public key (.pub extension).
Extract and convert the public key into PEM encoded PKCS8 format:
openssl rsa -in jwtRS256.key -pubout -outform PEM -out jwtRS256.key.pub && cat jwtRS256.key.pub
# How to generate JWT tokens
A JWT can encapsulate several pieces of information that the API requester communicates to the server. For Workato, what is essential is the Workato access key. It should be placed in the JWT header like this:
{
"alg": "HS256",
"kid": "d4aee74e131926682043395edecaf377765fae48e56e232cb295af475b314545"
}
The JWT is a signed representation of the JSON structure. The API requester is responsible for generating and packaging a JWT in the correct format.
ALTERNATIVE CLAIMS
In this example, the Workato access key is included in the header as the kid claim. Some identity providers may restrict the kid claim. If this is the case, you can include the access key in the payload section of the token, under one of the following claims: https://www.workato.com/sub, workato_sub or sub.
If these claims are used for other purposes in your use case, you may use a custom claim to hold the access profile key. Learn more about alternative claims.
Generate a JWT using the tool at JWT.IO (opens new window).
In the Algorithm dropdown, select either HS256 (HMAC) or RS256 (RSA).
Enter the JSON format text into the Payload field on the Decoded side of the tool:
{
"alg": "HS256",
"kid": "d4aee74e131926682043395edecaf377765fae48e56e232cb295af475b314545"
}
Paste your private key (RSA) or secret string (HMAC) in the Verify Signature section.
The signed and encoded key then appears in the Encoded section.
For example, a generated HMAC JWT might look like:
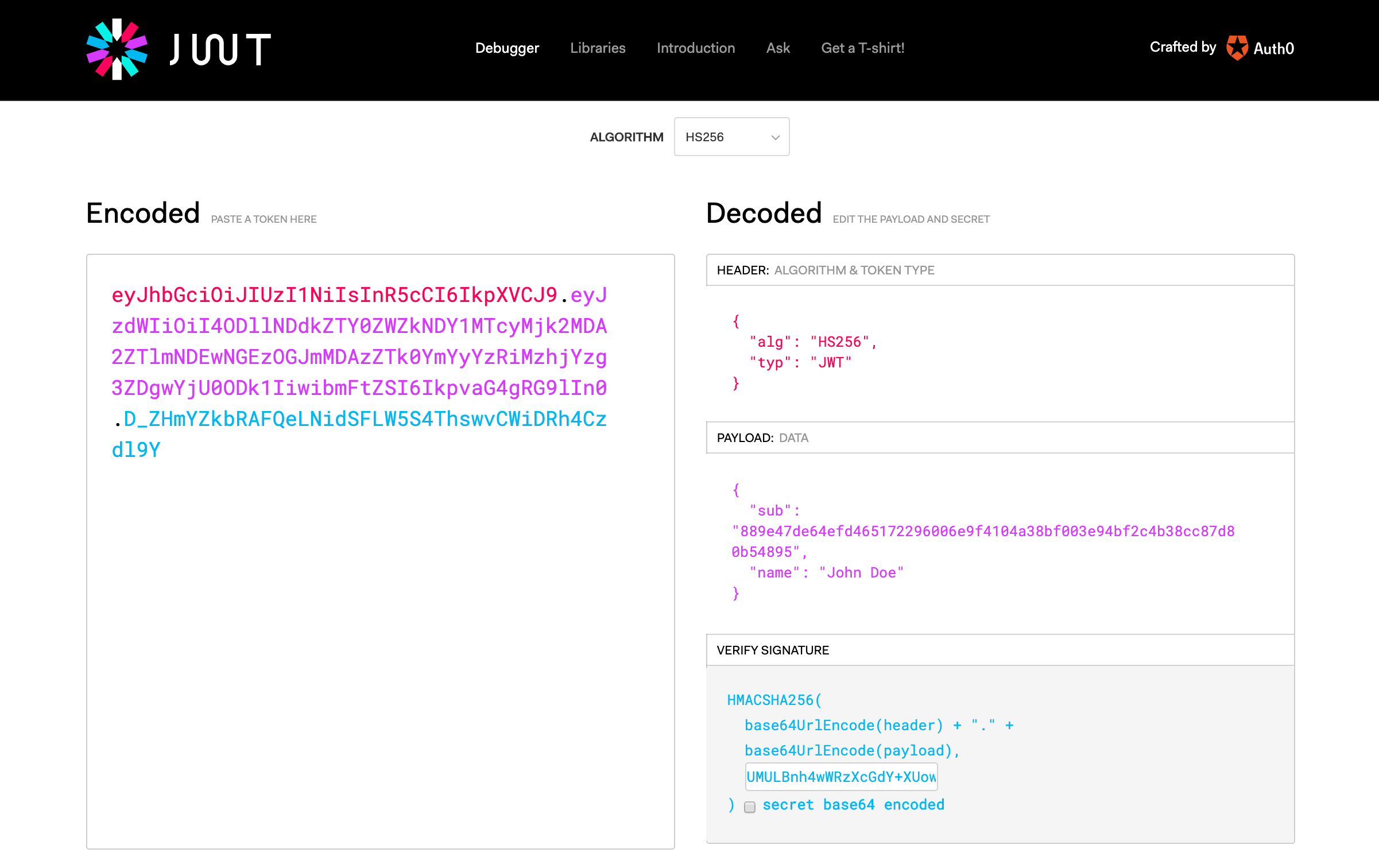 JWT Generation
JWT Generation
Similarly, an identity provider will be able to issue JWT with the API key embedded in the corresponding JWT claim. See JWT Workato claim for more information.
# Calling an API endpoint with JWT
The encoded and signed token is passed to the Workato API in the header (see Calling APIs). The access token is sent in the Authorization header with the Bearer authentication scheme.
Examples:
Postman:
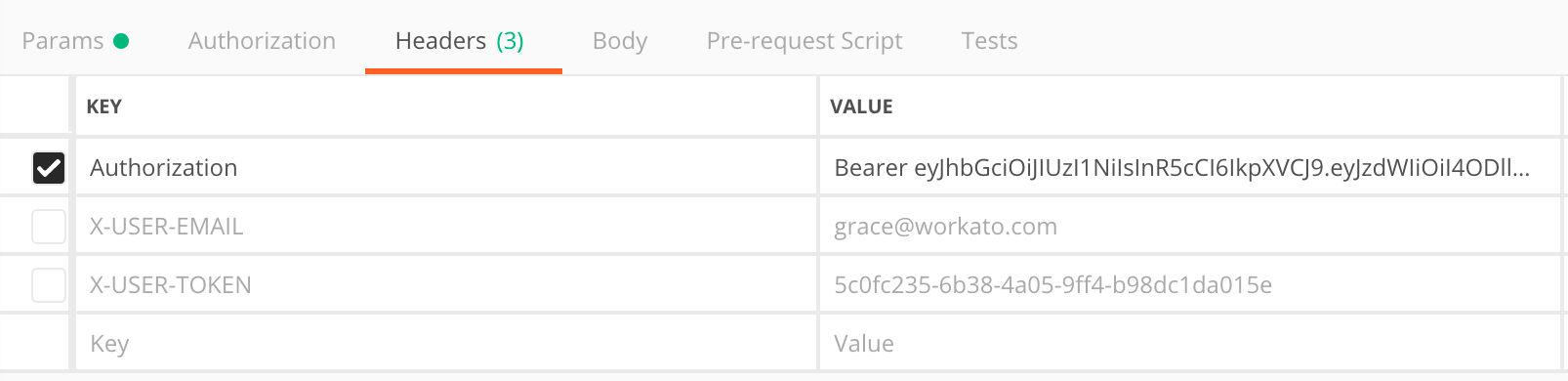 Example of a JWT used in Postman
Example of a JWT used in Postmancurl request:
curl -XGET \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer ayJhbGciOiJIUzI1NakIKjkJFVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiI4OJSIFMLLdkZTY0ZWZkNDY1MTcyMjk2MDA2ZTlmNDEwNGEzOGJmMDAzZTk0YmYyYzRiMzhjYzg3ZDgwYjU0ODk1IiwibmFtZSI6os9fvaG4gRG9lIn0.D_ZHmYZkbRAFQeL' \ 'https://apim.workato.com/api-endpoints-v1/call?email=john-doe%40acme.com'
# Extracting JWT payload claims
Identity providers who manage employee identities often load several pieces of information about the subject, for example Email, Employee ID, or assigned Permissions or scopes. They are written in the JWT as payload claims.
The following example shows a decoded JWT payload. The sub claim is used to identify the Workato access profile, while the other claims are additional information about the API caller:
{
"sub": "588dec828cc4fc6f579e5252ca4a3acb3d24527efa588e0329a9490a0d1dc062",
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@acme.com",
"acme_id": "A0122152",
"admin": true
}
Workato will parse the JWT and read all payload claims. Priority will be given to standard claims (opens new window) and claims that are required for Access profile authentication. If the JWT exceeds the character limit, the payload will be truncated and some payload claims may no longer be accessible.
CHARACTER LIMIT
The character limit for the encoded JWT payload is 4096 characters. Requests containing JWT with larger payloads will fail with the following error:
{
"error": "JWT payload size exceeded (5358, max 4096)"
}
# How to extract JWT payload claims
In the recipe building phase, JWT payload claims are found in the JWT claims datapill.
Switch to Formula mode and parse the JWT claims datapill as a JSON object.
For example, use the syntax [JWT Claims]["email"] to extract the email claim:
Extract JWT payload claims
Payload claims will be automatically parsed at runtime.JWT payload claims parsed at runtime
Last updated: 5/2/2024, 8:17:51 PM